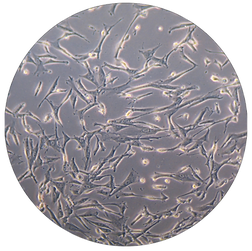
Mesenchymal Stem Cell
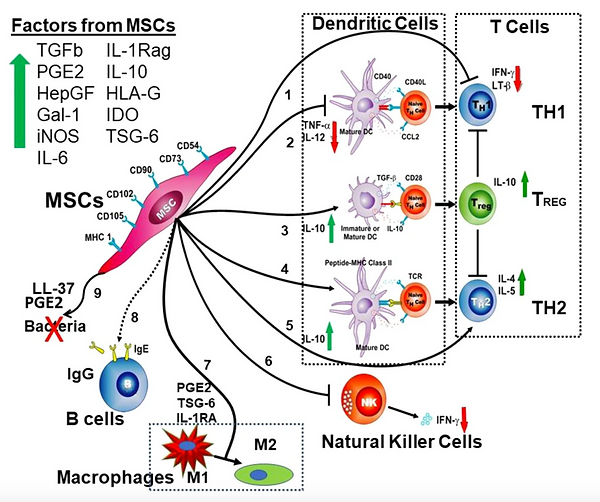
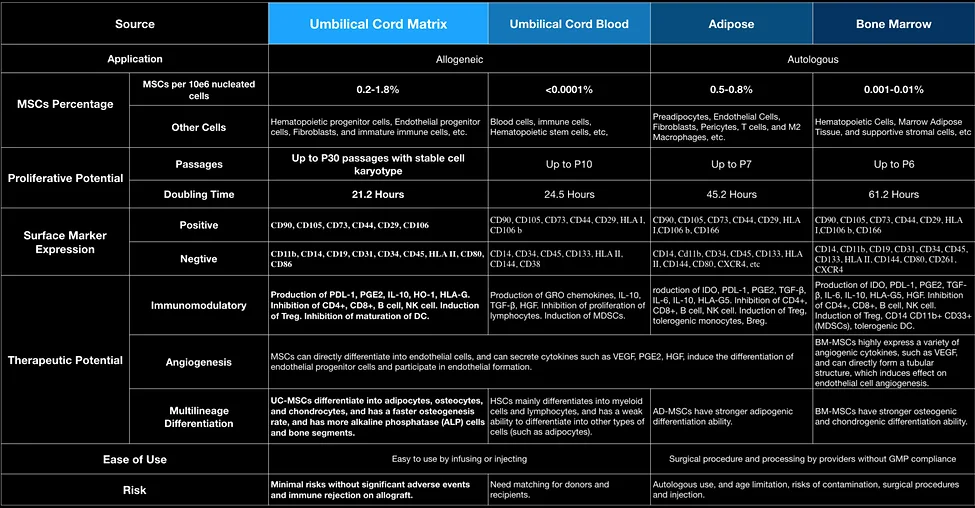
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a kind of multipotent adult stem cells that are distributed in the capillaries of multiple tissues of the human body and have the ability to self-renew, multi-lineage differentiation and secretome. Many researchers consider the transplantation of MSCs to be the most effective tool for cell therapy.